Overview
 | Autonomous mobile robots essentially perform three tasks: sense, think, and act. These three tasks include communication with sensors to obtain data from the robot's environment, execution of algorithms for localization and planning, and driving actuators to control the robot's motion. LabVIEW addresses each task by providing drivers for interfacing with sensors, tools for developing or reusing existing algorithms, and integration with NI hardware for driving motors. |
Table of Contents
Sense
From data acquisition to sensor fusion, learn how to combine the power of LabVIEW with graphical system design to quickly and efficiently complete the perception phase of your robotics application.
Lidar
 | Light Detection & Ranging is a remote sensing technology that uses the time delay and scattering properties of reflected laser pulses to identify characteristics of surrounding objects. |
Camera (CCD and CMOS)
| CCDs and CMOS image sensors use photo-active regions to read light characteristics in order to generate images. They provide the capability for environmental analysis, navigation, object identification and tracking. |  |
More Articles Related to Sensors and Perception
 | View extensive documentation that provides in-depth knowledge on sensors for mobile robots, localization and inertial sensing and signal processing as it pertains to robotics. |
Think
Take advantage of custom algorithm development, analysis, and visualization as you learn how to capitalize upon a full suite of LabVIEW tools for navigation, mapping and more.
Planning and Navigation
 | Planning and navigation for an autonomous mobile robot involves purposeful decision-making and execution that a system utilizes to achieve its highest-order goals. |
Autonomous Map Building
| Autonomous map building is when a robot generates a map of the environment using sensor information, while localizing itself relative to the map. | 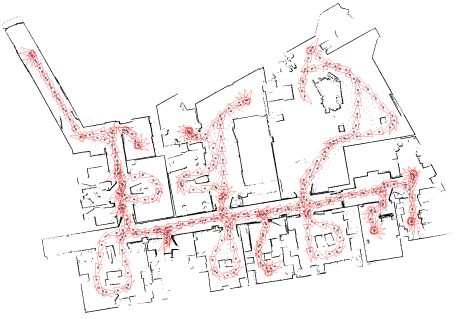 |
Localization
 | Localization allows autonomous mobile robots to determine their position in the environment. These robots usually follow two types of approaches: behavior-based navigation and map-based navigation. |
Machine Learning
| Robots can be programmed to learn about their world just like a human child. Trial and error, test and compare, and success and failure are all methods that humans use. |  |
Multi-Robotics
 | An emerging field of robotics is the concept of autonomous robots operating as part of a greater group or swarm. The applications include search and rescue, rapid mapping of an area, or automated mine clearing. |
Act
Learn how to build advanced systems incorporating software capabilities such as control, communication, data logging, and signal processing while performing logic and motion.
Drive an Actuator
 | A robot uses actuators to perform physical actions such as transporting the robot from one place to another. |
Control Laws
| Control laws are used to dictate how a robot moves within its environment by sending commands to actuators. |  |
Self Optimization
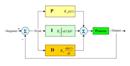 | The PID control algorithm is the basis for many advanced control algorithms and strategies used in robotics. For a PID control algorithm to have optimal performance, the PID controller must be properly tuned. |


Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar